Smart Goals for English Language Arts in Middle School
Sara Davila is a Learning and Language Acquisition Good with experience in education, researching, writing materials and training other teachers. Ane of her areas of language learning expertise is the Global Calibration of English . Sara has been sharing her height ten uses of the GSE Instructor Toolkit for language teachers in a serial of ten blog posts.
Today's article is number five in the top ten countdown. It provides a step-by-step guide to using the toolkit to aid your learners set up SMART linguistic communication learning goals.
—
The vast majority of language teachers have goals which are clear and defined for our learners. These goals might be informed by a national curriculum, the coursebook you are using, or the institution yous work for. Goal setting is fundamental to student success, providing a clear focus and framework for both teachers and learners as you progress through a form together.
However, learner goal setting is a little fleck dissimilar. Here, your role as the instructor is to guide students through the process of creating SMART goals for themselves. This will assist them attain their own recognizable and measurable progress.
What is a SMART goal?
The SMART procedure for goal setting is piece of cake to follow. To create SMART goals, your students need to define goals which are:
- Specific (articulate, detailed, factual, precise)
That means vague or generalised goals, like, "I want to improve my English language" are no practiced. You're looking for something specific from your students, such as, "I want to reach A2 level in English."
- Measurable (exam, assess, detect)
The next question to ask your students is, "Tin can this goal be measured?" In other words, how will your student know when they take succeeded? Well, in the example in a higher place, a exam would be a adept fashion of measuring progress to encounter if your student has moved up a level afterward studying hard.
- Achievable (realistic, grounded, possible)
Getting to an A2 level is a good example of a realistic goal for an A1 or an A1+ pupil. Aiming for a B2 level would be unrealistic in the brusk term. It'due south important that students feel challenged by their goal – but that the goal is all the same achievable.
- Relevant (of import, valuable, personal)
The goal should have personal significance for the student, and so it'south important to let students choose their ain goals, for their own reasons. Don't be tempted to make suggestions based on the goals that you would like to see them reach!
- Timely (deadline, time limit, agenda goal)
It's no skilful setting a goal without a deadline. Encourage your student to ready themselves a date in the future. With the goal of moving upwards a level, for example, you could say, "Ok, yous can sit a level test in three months and see if you've accomplished A2 level."
Larn more virtually SMART goals for language students .
How does the GSE Instructor Toolkit help create SMART goals?
Setting goals in a language classroom tin can exist difficult when students don't speak the language they are trying to set goals in. How can an English learner apply English to define their goals if they are even so learning to speak, read, listen and write?
This is where the Global Calibration of English Teacher Toolkit can actually help teachers and students.
The GSE Teacher Toolkit can support teachers and learners by:
- clearly describing what a learner can do at the moment
- outlining what a learner could do in the futurity
To practice this, we need to have students browse through the Global Scale of English and focus on identifying what they tin currently do:

- Open the GSE Teacher Toolkit .
- Help learners select their learning program; Full general Adult, Academic, Professional, or Young Learner.
- Accept them motion the GSE ruler to match their current level. For example, students who are currently A2 should await at the skills in the 30-36 GSE range. You can also click on a CEFR level to chop-chop select the CEFR range.
- Finally, have students choose a skill they desire to piece of work on. For this practice, it's best if students review one skill at a time, for example speaking. They tin can choose between language skills (reading, writing, listening, speaking) or enabling skills (grammar and vocabulary).
One time your students accept chosen the level, click evidence results to come across learn more:
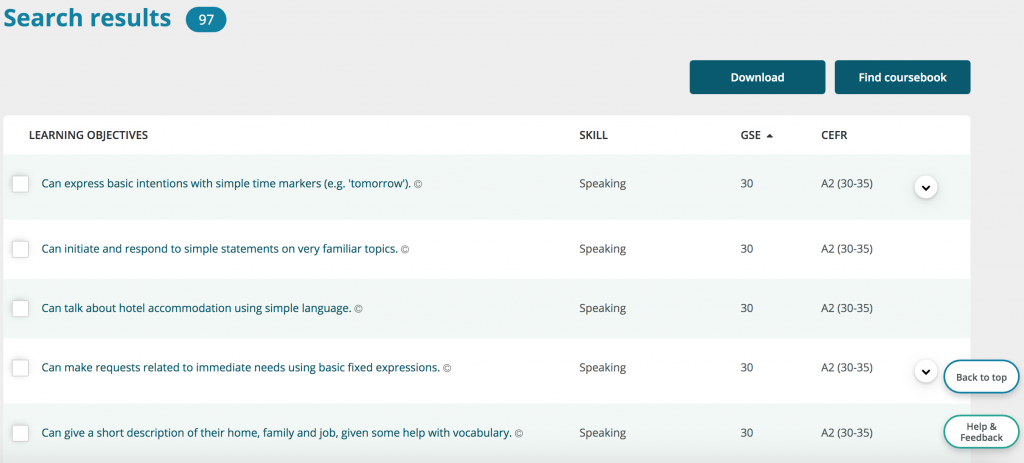
Now, you can take advantage of some of the dynamic features of the GSE Teacher Toolkit , specifically being able to check learning objectives.
Ask students to review the listing of learning objectives in society for them to:
- Check the box when they know they can practice information technology
- Check the box when they know they want to do it
This keeps students focused on what they tin do at present, and what they want to do in the future. And information technology's an piece of cake way for students to see what SMART English goals expect like.
If you get your learners to review the GSE Teacher Toolkit to create their goals, you can ensure that your classes are relevant to students' goals and focused on the skills that students want to learn.
And this activity can however work with distance learning, or a flipped classroom. Simply ask students to review the GSE Teacher Toolkit before coming together for class. When class begins, your learners tin share their downloaded list of objectives.
Helping students to accomplish their SMART goals
Now you tin collate all the objectives that students desire to achieve, noting popular goals equally you practise so. Compare what your learners want to reach with the electric current learning plan and objectives you accept for your course. You can utilize this data to aid your learners understand the timeframe in which they will be working towards their goals. And, if there are goals that aren't part of your learning plan, you can include them if they're an objective for a bulk of students. Otherwise, it's an opportunity for i-to-ane planning to help support individual learning goals and set up timelines that are reasonable for your students.
Setting SMART goals volition aid your students take ownership of their learning and feel motivated to become their heads down. Goal-setting is a critical step in the language learning process, and has been shown to help students increase their efforts and accomplish greater success. So why not attempt setting some goals with your students this term using the GSE Instructor Toolkit ?
Farther reading
You tin can notice more practical tips on using the GSE Teacher Toolkit on our blog. Other articles in the Top 10 countdown offering insights into using the toolkit to teach grammar and vocabulary . Get inspiration for your lesson plans , and address curriculum standards with the help of the GSE Instructor Toolkit.
Source: https://www.english.com/blog/gse-teacher-toolkit-top-10-helping-learners-set-smart-goals/
0 Response to "Smart Goals for English Language Arts in Middle School"
Enviar um comentário